Explain How Differences in Density Can Cause Cloud Formation
Clouds are denser than fog but there are times when fog can also become dense. 2 Clouds are also formed when air encounters mountains or other topography.

Ppt Earth Science 18 2 Cloud Formation Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 3037588
Due to its lower density it moves up over the colder northern air cooling as it rises.

. Evolution of planets can be understood in three stages. As the suns rays hit the ocean water evaporates into the gas phase. Density The density is also a major differentiating factor that segregates clouds from the fog.
Coalescence takes over as the falling drop starts to collide and merge with smaller droplets in its path. Clouds are caused mainly by the adiabatic cooling of air below its dew point. Explain different phases of evolution of planets.
They expand because they have a lower molecular weight. Explain three different ways a giant molecular cloud can be triggered to contract. During the day clouds can make the temperature on Earth cooler by blocking heat from the Sun.
This influence of aerosols on clouds is called the indirect effect and is a large source of uncertainty in projections of climate change. Water vapor attaches itself to aerosol particles floating in the air and condenses into a. Warm moist air masses are drifting due to their low density.
Clouds are formed when air containing water vapor is cooled below a critical temperature called the dew point and the resulting moisture condenses into droplets on microscopic dust particles condensation nuclei in the atmosphere. As it moves up and away from the heat source it cools and becomes more dense and sinks. In low pressure systems with their cyclonic anti-clockwise in the northern hemisphere air flow warm humid subtropical air is transported to the north-east.
Clouds have a density of 05gm3 and fog has a density of 05gm3 005gm3. We give these regions the highly technical name clumps. In meteorology a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of minute liquid droplets frozen crystals or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space.
The molecular cloud filaments can be up to 1000 light-years long. -The idea that the air is rising due to density -Convection refers to the vertical movement of the atmosphere due to density differences between and air parcel and the surrounding atmospheric environment Convective Cloud Base Formula Hm 125m T-To degrees Celsius Hft 222 ft T-To degrees Fahrenheit. At night clouds can make Earths temperature warmer by trapping heat that came from the Sun.
Convection cycles in the atmosphere drive cloud formation. 1 The first process is perhaps the simplest. Air that is less dense rises which causes lower air pressure.
3 The Cold Cloud Process In summary 4 steps in the cold cloud process 1. Low pressure forces air mass movement because it is light and contains less moisture. In air with high concentrations of aerosols water can easily condense on the particles creating a large number of small droplets right.
On Earth clouds are formed as a result of saturation of the air when it is cooled to its dew point or when it gains. The denser the air the more collisions there are between molecules because there is less room for them to avoid running into each other so we get more air pressure. Select all that apply shock waves passing through molecular clouds mutual attraction between dense cores collisions between molecular clouds the interstellar magnetic field the spiral arms of the Milky Way through which molecular clouds may pass.
As waters temperature increases in the presence of a heat source it will become less dense and rise. First well learn about some basic convective clouds known as cumulus clouds and then well learn about cumulonimbus clouds and thunderstorms. So you can see that density.
According to their height expanse density and transparency or opaqueness clouds are grouped under four types. The air is normally cooled by expansion during its upward movement. As the clouds are formed at some height over the surface of the earth they take various shapes.
This is how clouds form on the warm fronts of such pressure systems in the mid-latitudes. So cold and dry air masses are stable because they have a higher density and higher average molecular bulk. So clouds can have both a cooling effect and a warming effect.
Convective clouds are clouds that are formed by convection which is simply the process of warmer air rising since it is less dense than the surrounding atmosphere. Water or various other chemicals may compose the droplets and crystals. Currents are cohesive streams of seawater that circulate through the ocean.
The sun heats the earth and thus the air this warm air rises expands and cools forming clouds like in the image above. These clouds are dense very reflective and bright white. You can see this current by placing a dry.
Clouds are composed of large numbers of cloud droplets or ice crystals or both. Density and Convection at the Beach. More water vapor causes high humidity and less causes the.
Within the clouds are cold dense regions with typical masses of 50 to 500 times the mass of the Sun. The air becomes more stable and cloud formation changes. The average cloud droplet has a terminal fall velocity of 13 cm per second in still air.
Convection is heat transfer due to a density differential within a fluid. Within these clumps there. The gravitational force within the lumps leads to the formation of a core to the gas cloud and a huge rotating disc of gas and dust develops around the gas.
Its sort of like clouds are wrapping Earth in a big warm blanket. Because of their small size and relatively high air resistance they can remain suspended in the air for a long time particularly if they remain in ascending air currents. The stars are localised lumps of gas within a nebula.
Ocean currents can be caused by wind density differences in water masses caused by temperature and salinity variations gravity and events such as earthquakes or storms. Cloud condensation nuclei a few droplets can grow by condensation to the critical size where 3. The air rises and cools and again the air cannot hold all of the water it held when warm so clouds.
Some are short-lived and small while others are vast flows that take centuries to complete a. This happens because the land cools faster than the sea and as a result the air over land cools faster which creates an area of higher pressure on land and lower pressure over the sea. 10 Correct sample answer.
Cooling leading to saturation and condensation. Molecular clouds have a complex filamentary structure similar to cirrus clouds in Earths atmosphere but much less dense.

Cloud Formation Lifting Processes Atmospheric Lifting In Order For Air To Form Clouds The Air Must Be Lifted And Rise In Altitude There Are 4 Types Ppt Download

Cloud Formation Lifting Processes Atmospheric Lifting In Order For Air To Form Clouds The Air Must Be Lifted And Rise In Altitude There Are 4 Types Ppt Download
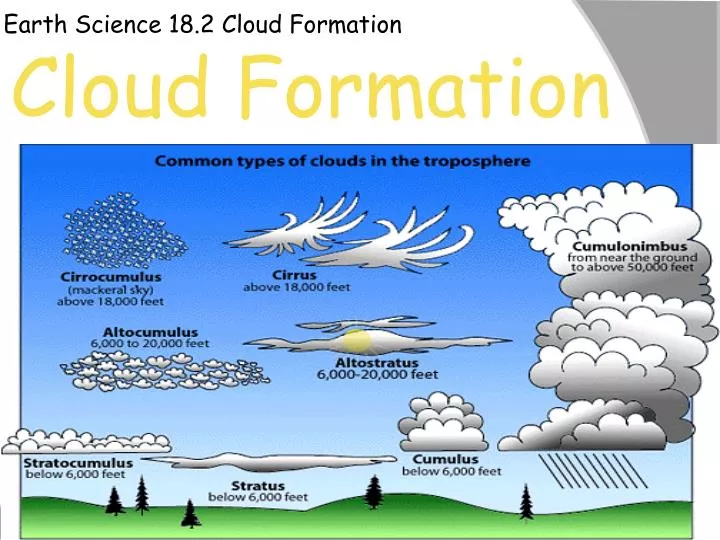
Ppt Earth Science 18 2 Cloud Formation Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 3037588
No comments for "Explain How Differences in Density Can Cause Cloud Formation"
Post a Comment